Abstract
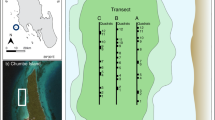
Understanding the temporal dynamics of seagrasses and the major influences on seagrass growth is critical for seagrass habitat conservation and administration. However, little work has been done regarding these issues in southern China. To examine inter-annual and seasonal variations of the intertidal Halophila ovalis community in southern China, we conducted quarterly sampling using the SeagrassNet methodology and assessed environmental conditions as well as direct anthropogenic impacts on the seagrass meadow from July 2008 to October 2014. Our study demonstrated strong inter-annual and seasonal dynamics of the intertidal seagrass meadow in the study area. Generally, the community performed best (highest seagrass cover, leaf area, shoot density, total biomass) in summer and worst in spring among the 4 seasons. The temporal variations in the seagrass community attributes (e.g. above-ground biomass) were significantly affected by precipitation, atmospheric visibility, and salinity, while leaf width was significantly negatively correlated with temperature, atmospheric visibility and salinity. Temperature was a major factor influencing the seagrass community (both macroalgae and seagrass), with temperature data showing an inverse relationship between seagrass and macroalgae. The above-ground: below-ground biomass ratio and leaf width of H. ovalis were the most sensitive plant parameters monitored when assessing environmental interactions. Human physical disturbances did not have a significant effect on seagrass dynamics in the study area. We concluded that long-term monitoring (like SeagrassNet) is valuable in understanding the relationship between environmental variables and seagrasses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcoverro T, Duarte CM, Romero J (1995) Annual growth dynamics of Posidonia oceanica - contribution of large-scale versus local factors to seasonality. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 120: 203–210
Alexandre A, Santos R, Serrao E (2005) Effects of clam harvesting on sexual reproduction of the seagrass Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 298: 115–122
Beer S, Mtolera M, Lyimo T, Björk M (2006) The photosynthetic performance of the tropical seagrass Halophila ovalis in the upper intertidal. Aquat Bot 84: 367–371
Boese BL (2002) Effects of recreational clam harvesting on eelgrass (Zostera marina) and associated infaunal invertebrates: in situ manipulative experiments. Aquat Bot 73: 63–74
Brun FG, Hernandez I, Vergara JJ, Perez-Llorens JL (2003) Growth, carbon allocation and proteolytic activity in the seagrass Zostera noltii shaded by Ulva canopies. Funct Plant Biol 30: 551–560
Cabaço S, Alexandre A, Santos R (2005) Population-level effects of clam harvesting on the seagrass Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 298: 123–129
Cardoso PG, Pardal MA, Lilleb AI, Ferreira SM, Raffaelli D, Marques JC (2004) Dynamic changes in seagrass assemblages under eutrophication and implications for recovery. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 302: 233–248
Collier CJ, Villacorta-Rath C, van Dijk KJ, Takahashi M, Waycott M (2014) Seagrass proliferation precedes mortality during hypo-salinity events: a stress-induced morphometric response. PLoS One 9:e94014
den Hartog C, Yang Z (1990) A catalogue of the seagrasses of China. Chin J Oceanol Limn 8: 74–91
Duarte CM (1991) Allometric scaling of seagrass form and productivity. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 77: 289–300
Duarte CM (2002) The future of seagrass meadows. Environ Conserv 29: 192–206
Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Krause-Jensen D, Olesen B (2006) Dynamics of seagrass stability and change. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 271–294
Erftemeijer PLA, Herman PMJ (1994) Seasonal changes in environmental variables, biomass, production and nutrient contents in two contrasting tropical intertidal seagrass beds in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Oecologia 99: 45–59
Fonseca MS, Kenworthy WJ, Thayer GW (1998) Guidelines for the conservation and restoration of seagrasses in the United States and adjacent waters. NOAA Coastal Ocean Office, Maryland, NOAA Coastal Ocean Program Decision Analysis Series No. 12, 222 p
Hillman K, McComb AJ, Walker DI (1995) The distribution, biomass and primary production of the seagrass Halophila ovalis in the Swan/Canning Estuary, Western Australia. Aquat Bot 51: 1–54
Huong TTL, Vermaat JE, Terrados J, Van Tien N, Duarte CM, Borum J, Tri NH (2003) Seasonality and depth zonation of intertidal Halophila ovalis and Zostera japonica in Ha Long Bay (northern Vietnam). Aquat Bot 75: 147–157
Jankowska E, Włodarska-Kowalczuk M, Kotwicki L, Balazy P, Kuliński K (2014) Seasonality in vegetation biometrics and its effects on sediment characteristics and meiofauna in Baltic seagrass meadows. Estuar Coast Shelf S 139: 159–170
Kim J-H, Kim SH, Kim YK, Park J-I, Lee K-S (2016) Growth dynamics of the seagrass Zostera japonica at its upper and lower distributional limits in the intertidal zone. Estuar Coast Shelf S 175: 1–9
Kim J-H, Park SH, Kim YK, Kim SH, Park J-I, Lee K-S (2014) Seasonal growth dynamics of the seagrass Zostera caulescens on the eastern coast of Korea. Ocean Sci J 49: 391–402
Kim YK, Kim SH, Lee K-S (2015) Seasonal growth responses of the seagrass Zostera marina under severely diminished light conditions. Estuar Coast 38: 558–568
Kuo Y-M, Lin H-J (2010) Dynamic factor analysis of long-term growth trends of the intertidal seagrass Thalassia hemprichii in southern Taiwan. Estuar Coast Shelf S 86: 225–236
Lee K-S, Park SR, Kim YK (2007) Effects of irradiance, temperature, and nutrients on growth dynamics of seagrasses: a review. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350: 144–175
Lee SY, Kim JB, Lee SM (2006) Temporal dynamics of subtidal Zostera marina and intertidal Zostera japonica on the southern coast of Korea. Mar Ecol 27: 133–144
Lin HJ, Shao KT (1998) Temporal changes in the abundance and growth of intertidal Thalassia hemprichii seagrass beds in southern Taiwan. Bot Bull Acad Sin 39: 191–198
Liu F, Pang SJ, Chopin T, Xu N, Shan TF, Gao SQ, Sun S (2009) The dominant Ulva strain of the 2008 green algal bloom in the Yellow Sea was not detected in the coastal waters of Qingdao in the following winter. J Appl Phycol 22: 531–540
Marbà N, Cebrian J, Enriquez S, Duarte CM (1996a) Growth patterns of western Mediterranean seagrasses: species-specific responses to seasonal forcing. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 133: 203–215
Marbà N, Duarte CM (1998) Rhizome elongation and seagrass clonal growth. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 174: 269–280
Marbà N, Duarte CM, Cebrian J, Gallegos ME, Olesen B, SandJensen K (1996b) Growth and population dynamics of Posidonia oceanica on the Spanish Mediterranean coast: elucidating seagrass decline. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 137: 203–213
Marques LV, Short FT, Creed JC (2014) Sunspots drive seagrasses. Biol Rhythm Res 46: 63–68
Meling-Lopez AE, Ibarra-Obando SE (1999) Annual life cycles of two Zostera marina L. populations in the Gulf of California: contrasts in seasonality and reproductive effort. Aquat Bot 65: 59–69
NMDIS (2012) Tide table 2013 (vol. 3) from the Taiwan straits to the Beibu gulf. National Marine Data and Information Service (NMDIS), Ocean Press, Beijing, 587 p
Neckles HA, Short FT, Barker S, Kopp BS (2005) Disturbance of eelgrass Zostera marina by commercial mussel Mytilus edulis harvesting in Maine: dragging impacts and habitat recovery. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 285: 57–73
Nguyen VX, Detcharoen M, Tuntiprapas P, Soe-Htun U, Sidik JB, Harah MZ, Prathep A, Papenbrock J (2014) Genetic species identification and population structure of Halophila (Hydrocharitaceae) from the Western Pacific to the Eastern Indian Ocean. BMC Evol Biol 14: 92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-9292
Onuf CP (1996) Sea grass response to long-term light reduction by brown tide in upper Laguna Madre, Texas: distribution and biomass patterns. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 138: 219–231
Park SR, Kim S, Kim YK, Kang CK, Lee KS (2016) Photoacclimatory responses of Zostera marina in the intertidal and subtidal zones. PLoS One 11:e0156214. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0156214
Park SR, Kim YK, Kim J-H, Kang C-K, Lee K-S (2011) Rapid recovery of the intertidal seagrass Zostera japonica following intense Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) harvesting activity in Korea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407: 275–283
Qiu G, Fan H, Li Z, Liu G, Shi Y, Li S (2013) Population dynamics and seed banks of the threatened seagrass Halophila beccarii in Pearl Bay, Guangxi. Acta Ecol Sin 33: 6163–6172
Ralph PJ, Burchett MD (1995) Photosynthetic responses of the seagrass Halophila ovalis (R. Br.) Hook. f. to high irradiance stress, using chlorophyll a fluorescence. Aquat Bot 51: 55–66
Ralph PJ, Gademann R, Dennison WC (1998) In situ seagrass photosynthesis measured using a submersible, pulse-amplitude modulated fluorometer. Mar Biol 132: 367–373
Robbins BD, Bell SS (2000) Dynamics of a subtidal seagrass landscape: seasonal and annual change in relation to water depth. Ecology 81: 1193–1205
Short FT, Coles R, Fortes MD, Victor S, Salik M, Isnain I, Andrew J, Seno A (2014) Monitoring in the Western Pacific region shows evidence of seagrass decline in line with global trends. Mar Pollut Bull 83: 408–416
Short FT, Koch EW, Creed JC, Magalhaes KM, Fernandez E, Gaeckle JL (2006a) SeagrassNet monitoring across the Americas: case studies of seagrass decline. Mar Ecol 27: 277–289
Short FT, Mckenzie LJ, Coles RG, Vidler KP, Gaeckle JL (2006b) SeagrassNet manual for scientific monitoring of seagrass habitat (Worldwide edition). University of New Hampshire Publication, Durham, 75 p
Sidik BJ, Harah ZM, Fakhrulddin IM, Anuar MSK, Arshad A (2010) Growth performance of Malaysian’s spoongrass, Halophila ovalis (R.Br.) Hooker f. under different substrate, salinity and light regime. Coast Mar Sci 34: 103–107
SAQSIQ (2007) The specification for marine monitoring-part 4: seawater analysis. The State Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (SAQSIQ), China Standards Press, Beijing, 162 p
UNEP (2008) National reports on seagrass in the South China Sea. UNEP/GEF/SCS Technical Publication No. 12
Vermaat JE, Verhagen FCA (1996) Seasonal variation in the intertidal seagrass Zostera noltii Hornem.: coupling demographic and physiological patterns. Aquat Bot 52: 259–281
Xun Z, Ruan C, Yang Y, Fang B, Ou Y (2006) Tidal effects of groundwater levels in the coastal aquifers near Beihai, China. Environ Geol 51: 517–525
Zhang PD, Liu YS, Guo D, Li WT, Zhang Q (2016) Seasonal variation in growth, morphology, and reproduction of eelgrass Zostera marina on the eastern coast of the Shandong Peninsula, China. J Coastal Res 32: 315–322
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Liu P, Wang F, Liu B, Liu X, Yang H (2015) Temporal pattern in biometrics and nutrient stoichiometry of the intertidal seagrass Zostera japonica and its adaptation to air exposure in a temperate marine lagoon (China): implications for restoration and management. Mar Pollut Bull 94: 103–113
Zheng F, Qiu G, Fan H, Zhang W (2013) Diversity, distribution and conservation of seagrass species in China. Biodivers Sci 21: 517–526
Zhou Y, Liu X, Liu B, Liu P, Wang F, Zhang X, Yang H (2015) Unusual pattern in characteristics of the eelgrass Zostera marina L. in a shallow lagoon (Swan Lake), north China: implications on the importance of seagrass conservation. Aquat Bot 120: 178–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, G., Short, F.T., Fan, H. et al. Temporal variation of intertidal seagrass in southern China (2008–2014). Ocean Sci. J. 52, 397–410 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0039-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0039-y